• Principles and philosophy of mathematical simulation modeling. Model conceptual representation, functional representation (fundamental environmental transport and chemical processes) and computational representation (prototype representation, forcing functions, numerical solution techniques).
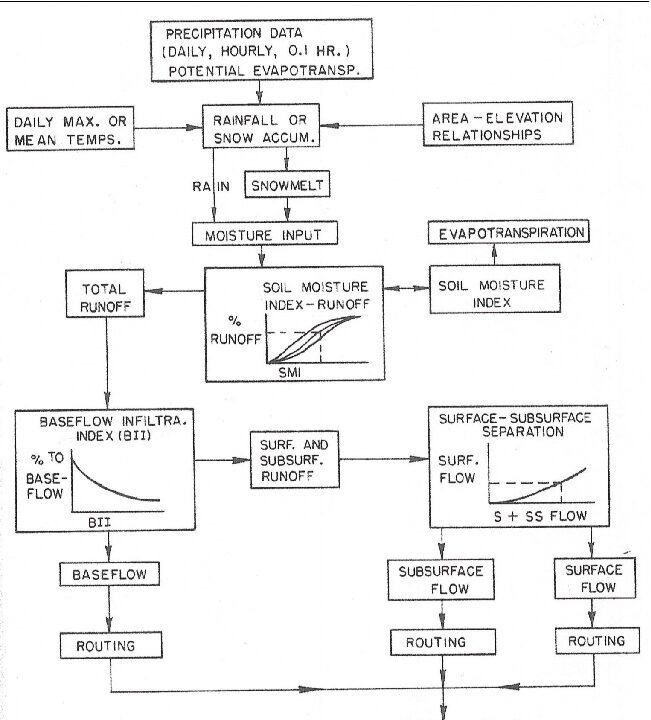
• Agrometeorological and hydrological simulation and modeling. Overview. The hydrologic cycle and its components. The stochastic nature of hydrological processes. Rainfall as part of agrometeorological and hydrological models. Basic rainfall-runoff models in agricultural and forest areas. Snow and snowmelt in modeling. Infliltration. Governing equations. Approximate models and numerical methods. Surface runoff, storage and routing. Overland Flow Theory. Watershed Modeling Approaches. Simulating runoff with lumped models. Evapotraspiration models. Subsurface Water Flow Theory. Erosion and sedimentation processes. Interrill processes, Rill erosion processes, channel processes. Interfacing the erosion model with the hydrological model. Water quality modeling, transport and chemical processes. Agronomic and crop processes and modeling.
• Model categories and classification. Selected models (see ‘References). Overview and demonstrative applications.
• Applications of selected well known models (see ‘References’) in typical case studies of agricultural areas with emphasis on their main simulation parameters (weather and climate factors, soil and crop characteristics, cropping system management techniques, etc).
Papers, Books and Technical Reports:
• Ambrose, R., Tsiros, I., Wool, T. 2005. Modeling Mercury Fluxes and Concentrations in a Georgia Watershed Receiving Atmospheric Deposition Load from Direct and Indirect Sources, J. Air & Waste Manage. Assoc. 55, 547-558.
• Ambrose, R. and Wool T. 2017. The Water Analysis Simulation Program (WASP). Version 8. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Athens, Georgia, USA.
• Better Assessment Science Integrating Point and Non-point Sources (BASINS model). https://www.epa.gov/hydrowq/better-assessment-science-integrating-point-and-non-point-sources-basins
• Chapra S. C., Pelletier G. J. and Tao H. 2006. QUAL2K: A Modeling Framework for Simulating River and Stream Water Quality, Version 2.04: Documentation and Users Manual, Civil and Environmental Engineering Dept., Tufts University, Medford, MA., March 7, 2006, 101 p
• EPIC: A Crop & Soil Productivity Simulation Model. https://epicapex.tamu.edu/
• National Research Council, 1991. Opportunities in the Hydrologic Sciences, National Academy Press, Washington DC, USA
• The Soil & Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) Model. https://swat.tamu.edu/
Scientific Journals:
• Journal of the American Water Resources Association
• Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association
• Modelling & Software
• Ecological Modelling
• Water Resources Research
• Agricultural and Forest Meteorology
• Journal of Hydrology
• Hydrological Sciences Journal
• Hydrology and Earth System Sciences
Laboratory Head with research work on Urban Bioclimatology, Agrometeorology and Hydrology, Environmental Modeling and Historical Climate Data Analysis