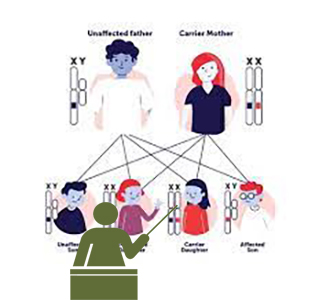
This is a basic course that presents the principles of Genetic Diseases. It aims to introduce students to the basic approaches for understanding the Genetics of inherited diseases, genetic diagnostics and modern therapeutic approaches.
It also reports extensively to the genetic, molecular and chromosomal basis of monogenic inherited diseases, diseases with complex inheritance, and cancer. Finally, the aim of the course is the understanding of the importance of basic principles of genetic diseases as a basis for application of diagnosis, personalized medicine, and novel treatments.